The Issue
Modern technologies have the promise to transform agriculture and food systems, improving the lives of millions. But how can products developed using these new techniques be introduced responsibly? Many governments lack the risk assessment experience needed to assure decision-makers and the public that environmental and food safety concerns have been properly addressed.
What We Are Doing
The Agriculture & Food Systems Institute develops knowledge resources and provides customized training to scientists, risk assessors, and regulators, to promote science-based risk assessments of products of biotechnology.
Why It’s Important
Governments and others need to have the tools to evaluate products of new technologies in order to make appropriate decisions for their populations so that the sustainable production of food, fuel, and fiber may be safely realized.
Program Staff

Andrew Roberts, Ph.D.

Bhavneet Bajaj, Ph.D., PMP
Collaborators & Partners
- Bangladesh Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
- Bangladesh Department of Environment
- Bangladesh Agricultural Research Council
- Biotech Consortium India Limited
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)
- India Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
- International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI)
- International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT)
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
- US Agency for International Development (USAID)
- US Department of Agriculture (USDA)
- University of Dhaka
- Philippines Bureau of Plant Industry
- Philippines Department of Agriculture
- Philippines Department of Science and Technology
- Philippines Food and Drug Administration
- Philippines Department of Environment and Natural Resources
- Biosafety Coalition of the Philippines
Programs
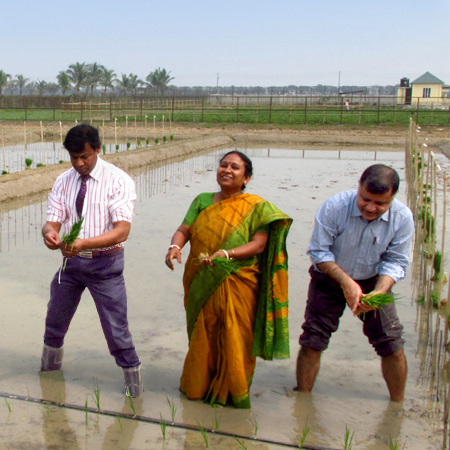

Strengthening Governance of Biotechnology in India & Bangladesh
We provide technical assistance to biosafety risk assessment and research communities and support government efforts to implement functional and scientifically sound regulatory processes for agricultural biotechnology.
LEARN MORE
Empowering Regulators with E-Learning Courses in Biosafety & Biotechnology
Our open access, interactive, self-paced courses provide training to help regulatory agencies, academics, and the private sector to better understand regulatory issues.
VISIT E-LEARNING
Advancing the Understanding of Biotechnology Issues
We regularly conduct trainings and workshops on a variety of topics to advance understanding of biotechnology issues. Programs are developed in collaboration with in-country partners to ensure they meet local needs.
LEARN MOREOur Successes
Biosafety regulations must evolve alongside scientific advancements to ensure the safe and transparent assessment of genetically engineered (GE) crops. In India, regulatory frameworks have been developed in response to emerging technologies, necessitating greater harmonization and accessibility of risk assessment processes. A need was recognized to strengthen biosafety capacity by supporting the development and adoption of key regulatory documents, improving transparency, and enhancing the technical expertise of regulatory scientists and risk assessors.
As part of the Phase II Capacity Building Project on Biosafety funded by the United Nations Environment Programme Global Environment Facility (UNEP-GEF) and at the request of the Government of India, the Agriculture and Food Systems Institute (AFSI) provided technical support to enhance environmental risk assessment (ERA) processes for genetically engineered crops.
In close collaboration with partners in India, AFSI provided technical support for:
- The development and adoption of three key documents that improve transparency of risk assessment and regulation of agricultural biotechnology in India.
- Workshops on problem formulation and other aspects of environmental risk assessment (ERA).
- A survey of the pipeline of genetically engineered crops in development in India.
- The development of a comprehensive set of resource documents, including eight crop-specific biology documents.
- An expert study tour to share experiences and learnings with the Office of the Gene Technology Regulator (Australia).
- An e-learning training program that serves both as a stand-alone resource for self-guided education and as a complement to India’s face-to-face training programs to raise awareness about the ERA guidelines.
-
Project Name:
UNEP-GEF Phase II Capacity Building Project on Biosafety
-
Years:
2014-2017
-
Funding:
Global Environment Facility through the United Nations Environment Program
-
Parties:
Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change, Government of India
-
Country:
India
Biosafety regulations often develop in response to the immediate needs of individual countries rather than through coordinated international efforts. Therefore, differences in institutional capacity, trade positions, public perceptions of biotechnology, and evolving scientific advancements have contributed to varied national regulatory approaches. Adding to this complexity, regulatory frameworks must continuously adapt to new scientific knowledge and emerging technologies. The Agriculture and Food Systems Institute (AFSI) recognized the need to equip stakeholders with the knowledge and tools to promote the harmonization and rationalization of biosafety regulations, fostering more consistent and science-based regulatory systems.
Funded by the World Bank, AFSI embarked on a project to support evidence-based decision-making by advancing technical capacity in eight countries.
The Partnership for Biosafety Risk Assessment and Regulation (PBRAR):
- Enabled stakeholders in Bangladesh, Colombia, Kenya, Paraguay, Tanzania, Uganda, Uruguay, and Vietnam to better promote harmonization and rationalization of biosafety regulations in their countries.
- Led to the publication of two OECD Consensus Documents, one on the biology of cassava and one on the biology of common bean, which are important tools used to inform risk assessments.
- Organized 26 national and regional workshops focusing on biosafety, risk assessment, and regulatory harmonization.
- Developed two e-learning courses on relevant biosafety topics.
- Provided more than 600 regulators, risk assessors, and other scientists with technical support and training.
As a result of this project, regulators from participating countries were enabled to substantively participate in regional and global biosafety forums. Below are a few examples of how the project improved the efficiency of national regulatory systems:
- Paraguay reduced its decision-making time by the national regulatory authority from two years to three months.
- Vietnam developed internal capacity to complete environmental review of new maize cultivars and approve these for cultivation.
-
Project Name:
Partnership for Biosafety Risk Assessment and Regulation (PBRAR)
-
Years:
2011-2014
-
Funding:
World Bank - Development Grant Facility
-
Parties:
Environment Directorate of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, World Bank, and Eight countries that had adopted or were considering the adoption of agricultural biotechnology.
-
Countries:
Bangladesh, Colombia, Kenya, Paraguay, Tanzania, Uganda, Uruguay, and Vietnam
“There has been an improvement of the capabilities of a large number of participants and the updates of the regulatory framework that are being implemented as a result of the activities that are being developed in the framework of the Partnership Program.”
The Biosafety Research in Pakistan Grants Program (BRPGP) recognized the need for biosafety research as part of a broader effort to support science-based decision-making and policy development. This program funded research that built local knowledge and established baseline data needed to support comparative assessments for agricultural biotechnology.
The Agriculture and Food Systems Institute (AFSI) managed the BRPGP, which was funded by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID).
Active from 2012-2014, this grants program:
- Supported research projects designed to improve understanding of the environmental parameters and agricultural practices that serve as a baseline to inform environmental risk assessment of genetically engineered plants.
- Provided 16 grantees from academic institutions in Pakistan with the support needed to develop important baseline data on agroecosystems and management practices.
- Helped build a knowledgeable community of practice to facilitate regulatory decision-making in the country.
-
Project Name:
Biosafety Research in Pakistan Grants Program (BRPGP)
-
Years:
2012-2014
-
Funding:
USAID
-
Parties:
Academic Researchers
-
Country:
Pakistan
Surrogate species are essential for evaluating the potential environmental impacts of new technologies, including assessing how genetically engineered crops may affect non-target organisms (NTOs). Selecting surrogate species requires careful consideration to ensure they represent key taxonomic or functional groups, and testing must be conducted with sufficient rigor to address the specific impacts under investigation. The Agriculture and Food Systems Institute (AFSI) recognized the importance of providing an experiential learning opportunity in laboratory and field testing of NTOs to scientists from academic and government research organizations.
AFSI, in cooperation with the United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service (USDA ARS), Iowa State University, and DuPont Pioneer, convened two five-day technical training workshops on non-target organism testing of transgenic crops in June 2013 and June 2014. This program provided regulatory scientists and environmental risk assessors with an opportunity to conduct practical experiments and data collection for both laboratory and field testing to evaluate risks to non-target organisms.
Using laboratory facilities provided by Iowa State University, workshop participants set up bioassays to assess the impacts of insect-resistant corn on corn earworm, the target pest, and on ladybird beetles, a beneficial non-target species. Three days later, participants returned to the lab to evaluate the bioassays, collect and compile their data, and draw conclusions.
As part of the workshop, participants:
- Learned how insect populations are assessed in agroecosystems using two common insect collection techniques: sticky cards to collect flying insects and pitfall traps to collect ground-dwelling insects.
- Set up the traps in established fields of insect-resistant and traditional corn.
- Reviewed and critiqued data generated by commercial laboratories, which are typically provided to government regulators in support of applications to authorize commercial planting of insect-resistant crops.
Both cohorts were surveyed prior to the workshop to establish a baseline of their knowledge and experience on the topics that would be presented during the program. Surveys were subsequently conducted four months and twelve months after the workshop in order to evaluate the longer-term impact on the participants’ professional development.
-
Project Name:
Practical Training in NTO Assessment for GE Plants
-
Years:
2013-2014
-
Funding:
World Bank - Development Grant Facility, USAID
-
Collaborators and Partners:
USDA Agricultural Research Service, Iowa State University, and DuPont Pioneer
-
Parties:
Scientists from Academic and Government Research Organizations
-
Countries:
Bangladesh, China, Ghana, India, Malawi, Nigeria, Pakistan and Uganda
“I am working on starting to collaborate with the Commission of Science and the Department of Environmental Science in Malawi, to make environmental risk assessment an integral part of agricultural production. Soon, Malawi will be rolling out Bt cotton in most parts of the country. This training program came at the perfect time.”
Discover
Publications
Frequently Asked Questions: Genome Edited Plants
Biosafety Resource Book Series | April 4, 2024
Published by the South Asia Biosafety Program, this booklet provides information about genome edited plants in a simple language, so readers may better understand the science, applications, and policies at the global and national levels.
Towards a Harmonised Approach to Food Safety Assessment of Genetically Engineered Plants in South Asia – Expert Working Group Report
December 20, 2021
The harmonisation initiative in South Asia was formally undertaken in 2020 by the Agriculture & Food Systems Institute (AFSI) by convening an Expert Working Group (EWG) constituted of senior experts and regulators identified from agencies in Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, and Sri Lanka that are relevant to the safety assessment of foods derived from rDNA plants. This report was systematically drafted by the EWG.
Frequently Asked Questions: Genetically Engineered Plants and Biosafety
Biosafety Resource Book Series | March 30, 2021
The South Asia Biosafety Program designed this booklet to address some of the questions the general public may have about the safety of genetically engineered plants, with explanations in easy and understandable language.
Biosafety Regulation and Processes in Bangladesh: A Guide for Researchers in Agricultural Biotechnology
Biosafety Resource Book Series | November 19, 2020
Part of the South Asia Biosafety Program’s capacity development interventions, this publication aims to inform researchers about the prevailing regulatory administrative system of Bangladesh and outlines the regulatory processes functioning at different stages of research and development of GE crops.
Paraguay’s Path Toward the Simplification of Procedures in the Approval of GE Crops
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology | August 18, 2020
This paper presents the recent evolution of the regulatory system in Paraguay toward the establishment of a simplified procedure for GE crops that have been already assessed by sound and experienced regulatory systems, taking into account several scientific criteria. Dr. Carmen Vicién, Agriculture & Food Systems Institute in-country partner, was a co-author of this paper, which references the Agriculture & Food Systems Institute’s involvement in the Partnership for Biosafety Risk Assessment and Regulation in Paraguay.
Sublethal Endpoints in Non-Target Organism Testing for Insect-Active GE Crops
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology | June 9, 2020
This review paper focuses on the current status and history of sublethal endpoint use in insect-active GE crops and evaluates the future use of sublethal endpoints for new and emerging technologies.
Genetic Biocontrol for Invasive Species
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology | May 25, 2020
This publication provides an overview of the state of genetic biocontrol, focusing on several approaches that were the subject of presentations at the Genetic Biocontrol for Invasive Species Workshop, which was sponsored by the OECD’s Co-operative Research Program on Biological Resource Management for Sustainable Agricultural Systems.
Agricultural Biotechnology and Biosafety in South Asia: Progress and Prospects
SAARC Agriculture Centre | September 30, 2019
This book contains the papers and proceedings of the SAARC Regional Consultative Meeting on the Progress and Prospects of Agricultural Biotechnology and Biosafety in South Asia, which took place on June 18- 20, 2019 in Dhaka, Bangladesh.
Problem Formulation for Gene Drive Mosquitoes Designed to Reduce Malaria Transmission in Africa: Results from Four Regional Consultations 2016–2018
Malaria Journal | October 15, 2019
This summary publication captures the findings from four African consultations organized by the New Partnership for Africa’s Development (NEPAD) to identify risk hypotheses and data needs for future environmental risk assessment of gene drives in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae.
OECD Consensus Document of the Biology of Mosquito Aedes aegypti
Safety Assessment of Transgenic Organisms in the Environment (Volume 8) | June 23, 2018
Volume 8 of the series Safety Assessment of Transgenic Organisms in the Environment contains the first OECD biosafety consensus document to deal with the biology of an insect, the mosquito Aedes aegypti.
Capacities for the Risk Assessment of GMOs: Challenges to Build Sustainable Systems
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology | April 5, 2018
The need for functional risk assessment bodies in general, and in the biosafety field in particular, demands continued efforts and commitment from regulatory agencies, if results that are sustainable in time are to be achieved. Dr. Carmen Vicién, Agriculture & Food Systems Institute in-country partner, was a co-author of this paper, which references the Agriculture & Food Systems Institute’s involvement in the Partnership for Biosafety Risk Assessment and Regulation in Paraguay and the use of Agriculture & Food Systems Institute eLearning courses in Kenya.
Results from the Workshop “Problem Formulation for the Use of Gene Drive in Mosquitoes”
American Journal of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene | November 29, 2016
Reducing the incidence of malaria has been a public health priority for nearly a century. However, before new technologies and associated vector control strategies can be developed and exploited, it will be necessary to understand and assess the likelihood of any potential harms to humans or the environment. To begin this process, the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health and the Agriculture & Food Systems Institute organized an expert workshop to consider the potential risks related to the use of gene drives in Anopheles gambiae for malaria control in Africa.
Events
-
 Second Capacity Building Workshop on Food Safety Assessment of Genetically Engineered Plants
Second Capacity Building Workshop on Food Safety Assessment of Genetically Engineered PlantsJune 3, 2025-June 4, 2025
New Delhi, India
-
 Bangladesh Stakeholder Consultation on Agricultural Biotechnology
Bangladesh Stakeholder Consultation on Agricultural BiotechnologyDecember 4, 2024
Dhaka, Bangladesh
-
 Workshops on Standard Operating Procedures for Research and Release of Genome Edited Plants in Bangladesh
Workshops on Standard Operating Procedures for Research and Release of Genome Edited Plants in BangladeshApril 22, 2024-April 23, 2024
Dhaka, Bangladesh
-
 Workshop on Standard Operating Procedures for Research and Release of Genome Edited Plants in Bangladesh
Workshop on Standard Operating Procedures for Research and Release of Genome Edited Plants in BangladeshFebruary 13, 2024
Dhaka, Bangladesh